Wilson
FRF Addict
you the man
size matters I like the fact it is smaller the question is is it lighter?
also I'm thinking it works like a look below
Centrifugal clutch
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
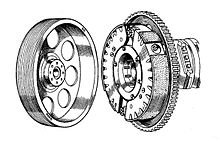

Talbot cars 'Traffic Clutch' of the 1930s
A centrifugal clutch is a clutch that uses centrifugal force to connect two concentric shafts, with the driving shaft nested inside the driven shaft.
The input of the clutch is connected to the engine crankshaft while the output may drive a shaft, chain, or belt. As engine revolutions per minute increase, weighted arms in the clutch swing outward and force the clutch to engage. The most common types have friction pads or shoes radially mounted that engage the inside of the rim of a housing. On the center shaft there are an assorted number of extension springs, which connect to a clutch shoe. When the center shaft spins fast enough, the springs extend causing the clutch shoes to engage the friction face. It can be compared to a drum brake in reverse. This type can be found on most home built karts, lawn and garden equipment, fuel-powered model cars and low power chainsaws. Another type used in racing karts has friction and clutch disks stacked together like a motorcycle clutch. The weighted arms force these disks together and engage the clutch.
When the engine reaches a certain speed, the clutch activates, working somewhat like a continuously variable transmission. As the load increases, the speed drops, disengaging the clutch, letting the speed rise again and reengaging the clutch. If tuned properly, the clutch will tend to keep the speed at or near the torque peak of the engine. This results in a fair bit of waste heat, but over a broad range of speeds it is much more useful than a direct drive in many applications.


A chainsaw clutch. The chain wraps around a sprocket behind the clutch that turns with the outer drum.
Centrifugal clutches are often used in mopeds, underbones, lawnmowers, go-karts, chainsaws, and mini bikes to
size matters I like the fact it is smaller the question is is it lighter?
also I'm thinking it works like a look below
Centrifugal clutch
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search


Talbot cars 'Traffic Clutch' of the 1930s
A centrifugal clutch is a clutch that uses centrifugal force to connect two concentric shafts, with the driving shaft nested inside the driven shaft.
The input of the clutch is connected to the engine crankshaft while the output may drive a shaft, chain, or belt. As engine revolutions per minute increase, weighted arms in the clutch swing outward and force the clutch to engage. The most common types have friction pads or shoes radially mounted that engage the inside of the rim of a housing. On the center shaft there are an assorted number of extension springs, which connect to a clutch shoe. When the center shaft spins fast enough, the springs extend causing the clutch shoes to engage the friction face. It can be compared to a drum brake in reverse. This type can be found on most home built karts, lawn and garden equipment, fuel-powered model cars and low power chainsaws. Another type used in racing karts has friction and clutch disks stacked together like a motorcycle clutch. The weighted arms force these disks together and engage the clutch.
When the engine reaches a certain speed, the clutch activates, working somewhat like a continuously variable transmission. As the load increases, the speed drops, disengaging the clutch, letting the speed rise again and reengaging the clutch. If tuned properly, the clutch will tend to keep the speed at or near the torque peak of the engine. This results in a fair bit of waste heat, but over a broad range of speeds it is much more useful than a direct drive in many applications.


A chainsaw clutch. The chain wraps around a sprocket behind the clutch that turns with the outer drum.
Centrifugal clutches are often used in mopeds, underbones, lawnmowers, go-karts, chainsaws, and mini bikes to
- keep the internal combustion engine from stalling when the output shaft is slowed or stopped abruptly
- disengage loads when starting and idling.


